Digital maturity in manufacturing is an increasingly important aspect of commercial performance in the life sciences industry today. In this article, we will explore the reasons why digitization is so important for commercial success in this industry and examine some of the data that supports this relationship . We will also look at top-performing life sciences companies and ten technologies they are using to drive their success.
What Is Digital Maturity?
Digital maturity refers to an organization’s ability to use technology effectively to achieve its strategic goals and objectives. It is the measure of how well an organization has adapted its business processes and culture to the digital age. A digitally mature organization can leverage technology to optimize its operations, improve customer experience, and create new business models. It has a strong digital strategy, a well-defined roadmap, and a culture of innovation that promotes experimentation and continuous improvement.
Life sciences manufacturing is perfectly situated to benefit from digital technologies that accelerate time to market, reduce costs, and provide more accurate results for lower risk of noncompliance.
Regulators and industry groups agree. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) established the Office of Digital Transformation which aims to provide guidance on IT, data, and cybersecurity under the FDA’s purview. This change will help the agency keep pace with the companies it regulates as the life sciences industry adopts practices under the Pharma 4.0 model. Pharma 4.0 is an industry-specific framework that aims to bring the focus on digitalization and automation under Industry 4.0 to the life sciences sector. The model envisions deeper connection, transparency, and adaptivity through data.
Take the first step in your Digital Validation journey by downloading Kneat’s Digital Validation Handbook. Learn the various types of digital validation and how to implement them in your company.
Why Is Digitization Important for Commercial Success?
One of the primary reasons why digitization is so important for commercial success in the pharmaceutical industry is that it provides several critical enablers. Digitization makes it possible to optimize operations and manufacturing processes, improve efficiency, and reduce paper-related waste. This, in turn, leads to lower costs, higher yields, and faster time to market. By automating key aspects of the manufacturing process, companies can achieve greater control over their operations and make more informed data driven decisions, leading to better commercial outcomes.
Improving Supply Chain Efficiency
Contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) play an increasingly critical role in the life sciences industry, and technology is helping these organizations to achieve a competitive advantage, capture a greater share of the market, and achieve better commercial outcomes. Digitization is particularly important for generics production, where speed to market after patent expiry is critical to capturing market share. By leveraging digital technologies, like Kneat’s digital validation platform, CDMOs can optimize their processes, reduce costs and waste, and speed up the time it takes to bring new products to market. Find out how in our Case Study with industry disrupting biotechnology company ElevateBio.
Digital Innovation Is a High Strategic Priority
There is a growing body of data that supports the connection between good commercial performance and the uptake and use of digital systems in the life sciences industry. Deloitte’s Biopharma Digital Innovation Study 2021 surveyed 150 biopharma leaders to better understand their experience with digital technologies and the industry’s approach to digital innovation. Digital innovation is seen as a highly strategic priority with 77 percent of respondents signaling that their organization sees digital innovation as a competitive differentiator.
10 Technologies Driving Digital Manufacturing Today
Many top performing life sciences companies in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical devices verticals use wide range of technologies to drive digital manufacturing today, including:
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Digital validation systems
- Data lakes/hubs
- Cloud computing
- Virtual Reality/Augmented Reality (VR/AR)
- Digital twins
- Wearables
- Blockchain
- Quantum Computing
1. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT technologies enable separate manufacturing processes to be interlinked, ensuring data integrity. Today, almost a third of the top 20 pharma companies in the U.S. are leveraging the power of the IoT by implementing it in their manufacturing plants—from production through distribution—to collect and analyze massive amounts of data from their operations, which they can then use to refine their processes and products.
Janssen Pharmaceuticals, a unit of Johnson & Johnson, adopted IoT technologies to get U.S. Federal Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) approval for moving Prezista, an HIV medication, from batch to continuous manufacturing. Sensor technology allowed them to remove the requirement for separate testing and sampling steps in the manufacturing process, and reduced manufacturing and testing cycle time, as well as waste and environmental impact, and process risk.

2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being widely used in the life sciences sector to optimize its manufacturing processes and make better-informed decisions. For example, AI is helping industry leaders like Novartis increase patient access, improve customer experience, drive automation, provide predictive analytics, and detect potential misconduct. AI also can be used to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis, treatment protocols, drug discovery, drug development, patient monitoring, and patient care, improving patients’ lives and optimizing the entire healthcare ecosystem.
3. Digital Validation Systems
A fully digital validation system allows for automated documents which dramatically reduce the time it takes to complete validation cycles. By pre-loading templates, project maps, and other documentation, as much as 80 percent of required work can be done before validation begins.
Automated documents do more than streamline a process, they enable complex tracing related documentation, so users can see the full connectivity of any documents they wish to trace. Traceability matrices are time-consuming and cumbersome to produce and maintain manually, but when automated provide detailed visibility into, and control over, the interrelationships between documents without the
workload.
ALCOA+ principles can automatically be applied as well—from attribution through unique logins to auto-generated timestamped e-signatures.
Audits are an inevitable part of manufacturing in highly regulated industries and a digital validation solution can remove many pitfalls of audit preparation by automatically preparing an audit trail. Such
steps include:
- Maintaining a revision history for any document
- Documenting changes, such as creation, deletion, or approvals
- Storing test results and events
The traceability matrix also assists audit execution through the seamless navigation to relevant documents.
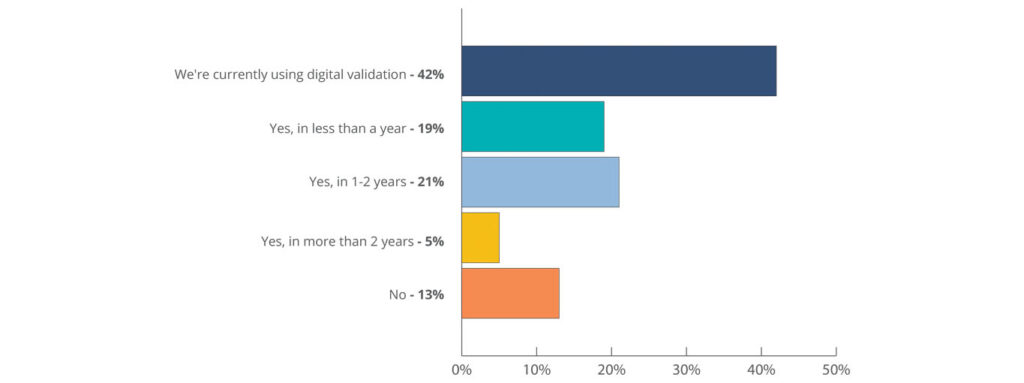
Fully digital validation systems are widely used in the life sciences industry today. The State of Validation 2022, a validation industry survey and report supported by CAI, Deloitte, Design Group, Kneat, and VEQTOR, found that 42 percent of respondents are already using digital validation to drive efficiency in their work today. This trend looks set to continue with a further 21 percent of all respondents signaling that they plan to adopt a digital validation system within the next one to two years.
Highly efficient validation accelerates the release of equipment, computer systems, and facilities to production. Whether sole product or multiproduct facilities, efficient changeover can result in higher yields, faster speed to market, and increased revenue. Learn more about the value of digital validation systems in our new Digital Validation Handbook.
4. Data Lakes/Hubs
Data lakes are centralized repositories that store large amounts of raw, unstructured, and semi-structured data. They enable organizations to store, process, and analyze vast amounts of data, providing a flexible and scalable solution for data management and analysis. Data lakes can be used for a wide range of purposes, including data exploration, machine learning, and business intelligence. Bristol-Myers Squibb, is one of several large pharmaceutical companies actively converting disparate data storage systems to large repositories.
Data lakes can also lead to greater connectivity across the manufacturing ecosystem. Looking to the future, validation data could be stored and curated in a way that makes it easily accessible to other teams, for use in future AI applications—like look ahead maintenance, based on performance. For example, using Kneat for CQV and equipment validation alone gives all stakeholders, including facilities and maintenance teams, a full lifecycle view. Kneat’s data gathering and reporting capabilities will create strategic and commercial value outside engineering.

5. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is widely used today within the manufacturing function at to facilitate daily work and 49 percent of Biopharma leaders are using this technology in day-to-day operations today. The cloud provides scalability and agility for businesses to facilitate communication and enable team collaboration from anywhere in the world with an internet connection. Data can be stored and shared securely. Cloud computing can even help to reduce costs and improve insights by enabling the collation of data for better visibility into manufacturing and supply chain operations.
6. Virtual Reality (VR)/Augmented Reality (AR)
The use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technology in the manufacturing industry is steadily increasing as companies learn how these technologies can increase efficiency, lower production costs, improve employee safety and training, enhance cross-company collaboration, and improve configuration, diagnostics, and reporting. In 2019 GlaxoSmithKline made use of AR technology to validate the design of a new aseptic manufacturing facility, ensuring that it complied with strict regulatory requirements. And new manufacturing workers can get familiar with the equipment and procedures at Pfizer’s new Modular Aseptic Processing (MAP) facility in Portage, Michigan thanks to VR without ever stepping inside.
7. Digital Twins
Some companies are using digital twins to simulate their manufacturing processes, which allows them to test and hone their operations in a virtual environment before putting them into play. In 2021 GSK successfully piloted the creation of a digital twin to improve its manufacturing process for vaccine adjuvants.
8. Wearables
Wearables commonly used in the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry are devices that connect workers throughout entire organizations with the data and tools needed to successfully collaborate and complete tasks safely and efficiently. They can help people to interact and capture data hands-free using vision, voice, and head gestures, which is particularly useful if they are operating in clean rooms in which limited tools are allowed.
Kneat partners with trusted suppliers of wearables which enable the use of, or integrates with, our digital validation software platform Kneat Gx. Learn more about our Technology Partners here.
9. Blockchain
The authenticity and integrity of data stored in blockchain networks gives this technology the potential to support data sharing, connectivity, and auditability across the life sciences manufacturing industry. 11 percent of Biopharma leaders signaled that they were using blockchain to facilitate their day-to-day work, with a further 59 percent having been part of a project that leveraged this technology.

10. Quantum Computing
Quantum computers can process data faster than ever to simulate complex interactions between biological molecules, expanding our ability to understand a range of disease mechanisms. Boehringer Ingelheim is one such company experimenting with quantum computing in pharmaceutical research and development (R&D), for molecular dynamics simulations.
Learn More
Digital maturity is an ongoing process that requires investment in technology, people, and processes, and organizations that achieve it are better equipped to compete in the fast-paced and constantly evolving digital economy.
If you’re looking to invest in digital validation technology, our new Digital Validation Handbook can help. It examines the various methods of digital validation, their benefits, and drawbacks.
Our guide also showcases how your business can adopt a digital validation system for faster, more accurate validation to underpin your organization’s commercial performance.




