Equipment validation is a crucial process in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that all equipment used in the manufacturing, testing, and production of pharmaceutical products consistently performs according to pre-defined requirements, specifications, and quality standards.
This process is not only a requirement for maintaining Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) but also a critical step in ensuring that the final products are safe, effective, and of high quality.
In this article, we will explore the importance of equipment validation in the pharmaceutical industry, key guidelines and regulations, the steps involved in an effective equipment validation process, and the benefits of digital equipment validation.
What Is equipment validation?
Equipment validation involves verifying that a piece of equipment meets the necessary requirements, specifications, and intended uses to ensure it aligns with user needs and complies with regulatory and safety standards. This process is typically conducted to adhere to quality management standards, e.g., ISO 13485, ISO 9001, regulatory standards (ICH, FDA), and industry best practices (ISPE).
Why equipment validation is important in the pharmaceutical industry
The primary goal of equipment validation is to ensure that the equipment performs reliably and consistently. This reliability directly translates to the quality of the pharmaceutical products being manufactured, tested, or stored. Without validated equipment, there is a risk of producing defective products that could fail to meet safety standards.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the stakes are incredibly high. Any deviation from standard operating procedures or the use of unvalidated equipment can lead to serious consequences, including product recalls, regulatory fines, or even harm to patients. Equipment validation is not just a regulatory requirement, it’s a fundamental part of quality assurance.
Regulatory requirements
Pharmaceutical equipment validation is mandated by several regulatory bodies worldwide, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The FDA’s equipment validation regulations emphasize that all equipment used in the production of pharmaceutical products must be validated to ensure they operate as intended and produce consistent results.
FDA equipment validation guidelines
- Risk-based approach: The FDA recommends a risk-based approach to equipment validation, focusing on the equipment that has the greatest impact on product quality.
- Documented evidence: The validation process must include documented evidence that the equipment performs as intended. This documentation is crucial for regulatory audits.
- Change control: Any changes to the equipment or processes must be carefully controlled and validated to ensure they do not negatively impact product quality.
- Regular revalidation: Equipment must be revalidated periodically to ensure it continues to operate correctly and produces consistent results over time.
GMP equipment validation
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are the backbone of pharmaceutical quality assurance, and equipment validation is a critical component of GMP, including Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) Regulations. GMP equipment validation ensures that all equipment used in the manufacturing process meets the strict quality standards required by regulatory bodies.
The equipment validation process

The equipment validation process in the pharmaceutical industry typically follows a structured approach that includes Requirement and Specification Generation, followed by Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ), and Performance Qualification (PQ). These three stages — collectively known as IQ OQ PQ — are critical in verifying that equipment is installed correctly, operates according to its specifications, and performs consistently under real-world conditions.
Requirement and specification generation
Requirement and Specification Generation is the first step in equipment validation in the pharmaceutical industry. It involves defining user requirements and technical specifications for the equipment to ensure it meets intended use and regulatory standards. This phase lays the foundation for subsequent validation activities, including IQ, OQ, and PQ.
Installation qualification (IQ)
Installation Qualification (IQ) is the first step in the equipment validation process. It involves verifying that the equipment has been installed correctly according to the manufacturer’s specifications and the company’s standards. During IQ, all components of the equipment, including wiring, plumbing, and mechanical parts, are inspected to ensure they are installed correctly and meet the required specifications.
Operational qualification (OQ)
Operational Qualification (OQ) follows IQ and involves testing the equipment to ensure it operates according to the predefined operational specifications. This stage verifies that the equipment functions correctly in all operating conditions, including normal and worst-case scenarios. OQ tests the equipment’s limits to ensure it can handle the full range of expected operating conditions without any issues.
Performance qualification (PQ)
Performance Qualification (PQ) is the final stage of the equipment validation process. During PQ, the equipment is tested under real-world conditions to ensure it performs consistently over time. This stage involves running the equipment under actual production conditions and monitoring its performance to confirm that it produces consistent, high-quality results.
Requalification and periodic review
Requalification involves reassessing the equipment to confirm it continues to operate within specified parameters. Periodic reviews ensure that equipment maintains compliance with regulatory standards and remains fit for purpose over time. These ongoing assessments help identify any need for maintenance, recalibration, or updates, ensuring consistent performance and product quality.
Equipment validation in laboratories

Laboratory equipment used in the pharmaceutical industry also requires validation to ensure the accuracy and reliability of test results. Laboratory equipment validation follows a similar process to production equipment validation, involving IQ, OQ, and PQ stages.
Test equipment validation
Test equipment validation is particularly important in pharmaceutical laboratories, where the accuracy of test results can directly impact product quality and safety. Validating test equipment ensures that it provides accurate and reliable results, which are essential for making informed decisions during the drug development and manufacturing process.
Developing an equipment validation protocol
An equipment validation protocol is a detailed document that outlines the steps, procedures, and acceptance criteria for the validation process. This protocol serves as a roadmap for the validation process, ensuring that all necessary steps are followed, and that the equipment is validated thoroughly.
Key components of an equipment validation protocol include:
- Purpose and scope: The protocol should clearly define the purpose of the validation and the specific equipment being validated.
- Responsibilities: It should outline who is responsible for each part of the validation process, including the preparation, execution, and review of the validation activities.
- Validation plan: This section should describe the validation approach, including the IQ OQ PQ stages, and the specific tests that will be conducted.
- Acceptance criteria: The protocol should define the criteria that must be met for the equipment to be considered validated.
- Documentation requirements: It should specify the types of documentation generated during the validation process, including test reports, calibration records, and deviation reports.
Equipment validation protocol template
Creating an equipment validation protocol from scratch can be time-consuming, so many pharmaceutical companies use a standardized equipment validation protocol template. These templates provide a structured format that can be customized to suit the specific needs of the equipment and the organization. A good template will include all the essential components mentioned above and should be flexible enough to accommodate different types of equipment and validation requirements.
Digital equipment validation
Digital equipment validation delivers many benefits, particularly in the pharmaceutical industry, where precision and compliance are critical.
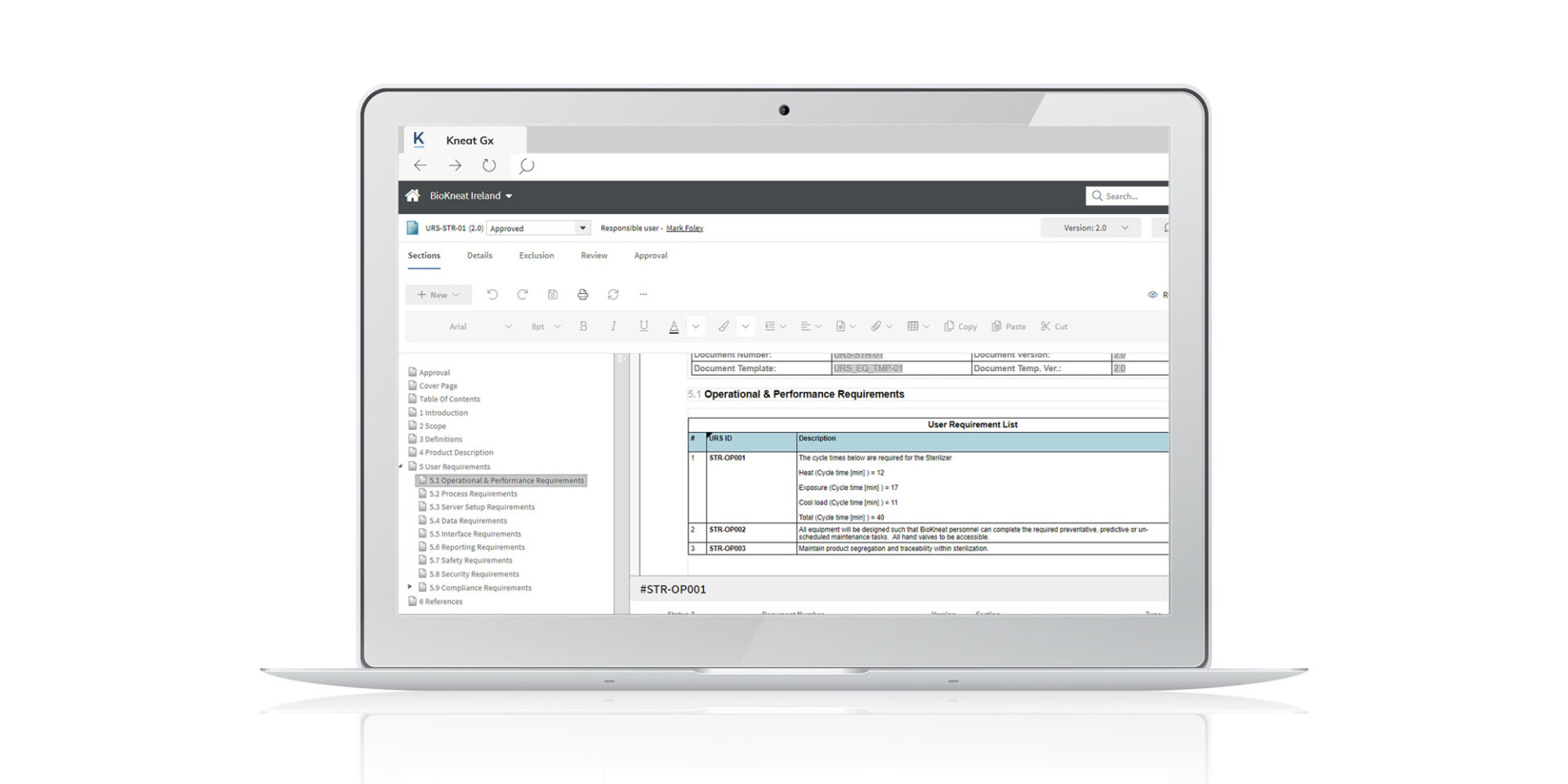
The advantages of digital equipment validation include:
- Efficiency and speed: Accelerates the equipment validation process, leading to significant productivity improvements and cycle time savings of up to 50%.
- Cost savings: Eliminates the need for paper records, reducing storage and retrieval costs.
- Real-time traceability: Ability to generate requirements and automatically build in traceability using our digital Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) ensures full coverage of testing of all requirements/specifications.
- Compliance and integrity: Enhances data integrity and compliance with ALCOA++ principles embedded in the process.
- Error reduction: Minimizes protocol GDP errors through digitized validation execution.
- Real-time insights: Offers instant macro and micro visibility into all aspects of the equipment validation process.
- Customization: Standardizes processes across sites while retaining flexibility for local site-specific needs.
- Audit readiness: Seamlessly prepare for audits by sending approved PDF documents to a secure digital room, allowing auditors to easily search, view, and interact with the content in real time.
Final thoughts
By adhering to a structured equipment validation process, including the IQ OQ PQ stages, and following industry regulations and guidelines, pharmaceutical companies can ensure compliance and the safety and effectiveness of their products. Digital equipment validation further enhances this process by streamlining operations, improving data accuracy, and providing real-time visibility.
To learn more about adopting an automated and data-driven approach to equipment validation at your organization, join our monthly demo webinar.




