Any validation or quality professional working in life sciences or highly regulated industries must be well versed in data integrity, its regulations, and the acronym so often associated with it: ALCOA. If you consider yourself typically up to speed on the subject (like I did) you may be surprised to hear of a new term: ALCOA++. (That’s two plusses).
What Is Data Integrity and ALCOA?
First, let’s go over what data integrity means in this context, and why it’s so closely associated with ALCOA.
Data Integrity: A term that refers to the quality of data used in the life sciences manufacturing lifecycle, specifically the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data. Data integrity rules for GxP documentation is a regulated by agencies depending on jurisdiction, including the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the U.S. and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the EU.
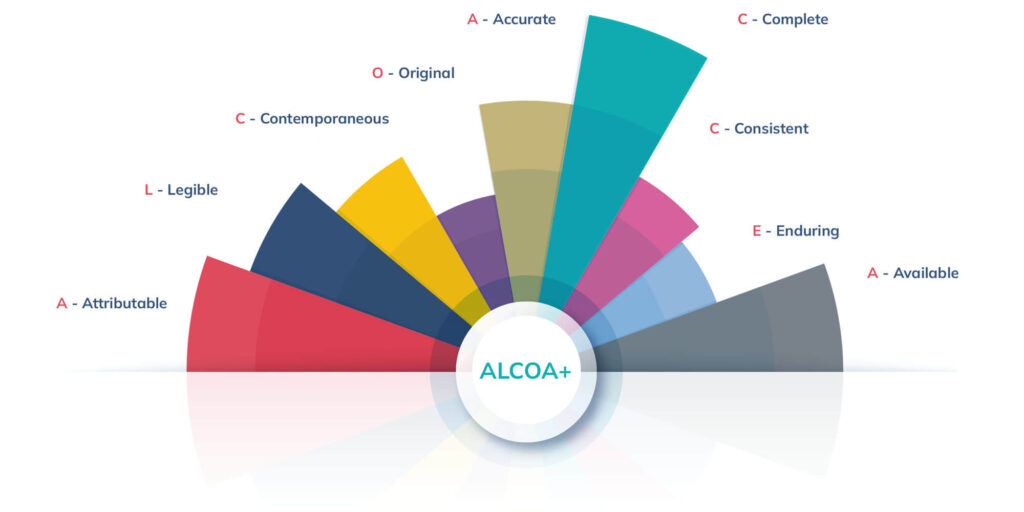
ALCOA: ALCOA is an acronym which stands for:
- Attributable: Activity can be traced back to a specific individual.
- Legible: Data is readable and able to be understood.
- Contemporaneous: Data is recorded in a timely manner.
- Original: Documents must be originals or “True Copies”.
- Accurate: Data accurately reflects what was recorded.
In recent years, ALCOA expanded to ALCOA+, the new gold standard for data integrity with the addition of four new criteria:
- Complete: Data is documented in its entirety.
- Consistent: Documents are orderly and chronological.
- Enduring: Documentation is stored for a significant period of time (often established by regulatory bodies).
- Available: Documents are accessible as needed.
ALCOA++
As infomercial salesmen say, “But wait, there’s more!” In 2023, an additional principle began showing up in conversations about ALCOA+: Traceable. While this may have elements that are addressed by the “available” principle, traceable goes more in depth. At a high level, a traceable document is one with a serviceable audit trail, with a clear line of activity which may include such actions as:
- Was the document revised?
- Why was the document revised?
- Is the original information able to be viewed?
Adding Traceability to Documentation
Some digital validation or quality systems, like Kneat Gx , can create a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTMs) which assist in traceability and document accessibility. Kneat’s Real-Time RTM , for example, can:
- Automatically track requirements and related tests based on selected folder.
- Provide at-a-glance insights into requirements and reference sections within Test Documents.
- Seamlessly deploy with no need to be configured or manually generated.
- Generate real-time updates as traceability attributes change.
- Deliver dynamic, granular view of data to make project management even easier.
These types of benefits would be nearly impossible to create using manual processes. The traceability principle for data integrity is even more reason to consider digital validation or quality solutions for highly regulated industries.
In the 2024 State of Validation Report , survey respondents identified “Compliance Burden,” “Audit Readiness,” and “Data Integrity” concerns as the top three main challenges in validation. In the same survey, 83 percent of respondents said they were currently using or planning to use digital solutions in their validation work in the near future.

Data Integrity Regulations
The FDA’s 21 CFR Part 11 regulation is the chief law governing data integrity for companies marketing to the U.S. In the EU, EudraLex Volume 4 Annex 11 governs the data integrity rules for computerized systems. These regulations are similar, being the product of international cooperation, and both are met by best practices associated with the GAMP 5 guidance produced by the International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering (ISPE).
Comparative Points
- Guidance Specificity: The FDA’s 21 CFR Part 11 is highly specific about electronic records and signatures, while the EU’s Annex 11 covers broader computerized system requirements.
- Enforcement Mechanisms: The FDA has a centralized enforcement mechanism, whereas the EU’s enforcement is carried out by individual member states, albeit guided by harmonized standards from the EMA. The FDA leans on 483 warning letters and the EU’s enforcement changes per jurisdiction.
- Focus on Electronic Records: Both regions emphasize the importance of maintaining integrity in electronic records, but the FDA’s guidance documents tend to be more detailed and prescriptive compared to the EU’s more principle-based approach.
Kneat’s Digital Validation Solution
Kneat’s digital validation solution is trusted by eight of the Top 10 global Pharma companies reducing cycle times by 40% or more, enhancing productivity, and ensuring compliance across all steps of the validation lifecycle.







