Summary
- Cleaning validation is a documented process that ensures pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment is free from contaminants like APIs, detergents, and microbial residues that could compromise product safety.
- Regulatory bodies including the FDA and EMA mandate cleaning validation, with non-compliance potentially leading to product recalls and facility shutdowns.
- A thorough risk assessment is essential to identify contamination sources, evaluate their impact, and implement effective control measures.
- Digital cleaning validation tools can reduce changeover time by up to 50% in multi-product facilities while ensuring data integrity and regulatory compliance.
- Medical devices also require cleaning validation, with protocols tailored to device materials, design, and intended use.
Cleaning validation is a critical process in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that manufacturing equipment is free from contaminants and residues that could compromise product safety and efficacy. This process is vital not only for compliance with regulatory standards but also for safeguarding public health.
In this article, we will explore the importance of cleaning validation in the pharmaceutical industry, key guidelines and regulations, the steps involved in effective cleaning method validation, sterilization validation, and the benefits of digital cleaning validation.
What Is cleaning validation?
Cleaning validation is a documented process that verifies the effectiveness and consistency of cleaning procedures used in manufacturing. It ensures that equipment is free of contaminants, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), detergents, and microbial residues, that could cross-contaminate subsequent batches of product. This validation is a requirement in the pharmaceutical industry due to the potential health risks associated with contaminated products.
Importance of cleaning in the pharmaceutical industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, cleaning validation is crucial for several reasons:
- Compliance with regulatory standards: Regulatory bodies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), mandate cleaning validation to ensure product safety and quality. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including product recalls and facility shutdowns.
- Product safety and quality: Cleaning validation ensures that products are safe for consumption by eliminating cross-contamination. It helps maintain the integrity and purity of pharmaceuticals, protecting consumer health.
- Risk management: Implementing cleaning validation helps identify potential risks associated with contamination and cross-contamination. It allows manufacturers to mitigate these risks effectively, ensuring the consistent quality of pharmaceutical products.
GMP cleaning and regulatory guidelines

Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are a set of regulations that guide the pharmaceutical industry in maintaining product quality and safety. GMP cleaning is an integral part of these practices, emphasizing the need for robust cleaning procedures and validation.
FDA cleaning validation guidelines
21 CFR cleaning validation
The 21 CFR cleaning validation regulations are part of the FDA’s requirements for pharmaceutical manufacturing. These regulations stress the need for validated cleaning procedures to prevent contamination and ensure product quality. They provide a framework for establishing and maintaining cleaning validation processes that meet regulatory expectations.
21 CFR Part 211.67 outlines the requirements for equipment cleaning and maintenance. These guidelines emphasize the importance of validating cleaning procedures to ensure that they are effective and reproducible. Key aspects of the FDA guidelines include:
- Establishing cleaning procedures: Define detailed cleaning procedures for each piece of equipment and product. These procedures should be based on the nature of the product and equipment.
- Validation protocols: Develop validation protocols that outline the objectives, scope, methodology, acceptance criteria, and responsibilities for cleaning validation.
- Sampling and testing: Implement appropriate sampling and testing methods to evaluate the effectiveness of cleaning procedures. Common methods include swab sampling and rinse sampling.
- Documentation and records: Maintain comprehensive documentation of cleaning validation activities, including validation reports, protocols, and test results.
Medical device cleaning validation
In addition to pharmaceuticals, cleaning validation is also crucial for medical devices. Medical device cleaning validation ensures that devices are free from contaminants that could harm patients or compromise device functionality. The process involves assessing the cleaning procedures used for medical devices and verifying their effectiveness.
Key considerations for medical device cleaning validation include:
- Device material and design: Consider the materials and design of the device, as they can affect the cleaning process and potential residues.
- Cleaning agents and methods: Evaluate the compatibility of cleaning agents and methods with the device materials to prevent damage and ensure effective cleaning.
- Validation protocols: Develop and implement validation protocols specific to medical devices, considering their unique characteristics and uses.
Cleaning validation risk assessment

A crucial aspect of cleaning validation is conducting a risk assessment to identify potential hazards and their impact on product quality. The risk assessment process involves:
- Identifying potential risks: Analyze the manufacturing process to identify potential sources of contamination, such as residual active ingredients or cleaning agents.
- Evaluating risk impact: Assess the severity and likelihood of contamination affecting product quality and safety.
- Implementing control measures: Develop strategies to mitigate identified risks, such as optimizing cleaning procedures and implementing monitoring systems.
- Continuous monitoring and review: Regularly review and update the risk assessment based on changes in the manufacturing process or regulatory requirements.
- Identifying risk-based strategies: Develop strategies to reduce testing requirements based on risk levels and comparisons against other equipment and product cleaning efficacies.
Cleaning method validation
Cleaning method validation is a systematic approach to confirm that cleaning procedures consistently remove contaminants to acceptable levels. It involves:
- Defining acceptance criteria: Establish clear acceptance criteria based on regulatory guidelines and product specifications.
- Developing validation protocols: Create detailed protocols that outline the validation process, including sampling methods, testing procedures, and acceptance criteria.
- Performing validation studies: Conduct validation studies to assess the effectiveness of cleaning methods, using appropriate sampling and analytical techniques.
- Documenting results: Maintain thorough documentation of validation studies, including test results and deviations, to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards.
Sterilization validation
Sterilization validation is another critical aspect of ensuring product safety in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries. It involves verifying that sterilization processes effectively eliminate all forms of microbial life, ensuring that products are safe for use.
Key steps in sterilization validation include:
- Defining sterilization parameters: Establish the parameters for the sterilization process, such as time, temperature, and pressure.
- Validation protocols: Develop protocols that outline the objectives, methods, and acceptance criteria for sterilization validation.
- Biological indicators: Use biological indicators to assess the effectiveness of the sterilization process.
- Routine monitoring and revalidation: Implement routine monitoring of sterilization processes and conduct periodic revalidation to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
Digital cleaning validation
With the advent of digital validation tools, the cleaning validation process has become more efficient and accurate, allowing for real-time validation and data analysis.
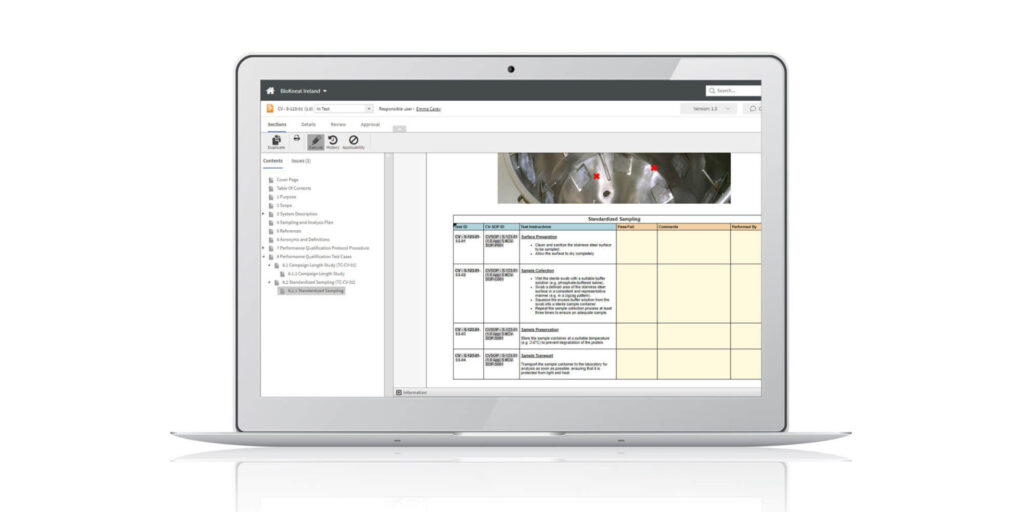
The advantages of digital cleaning validation include:
- Efficiency and speed: Reduces changeover time by up to 50% in multi-product facilities.
- Cost Savings: Eliminates paper records, storage, and retrieval costs.
- Real-time traceability: Ability to generate requirements and automatically build in traceability using our digital Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) ensures full coverage of testing of all requirements/specifications.
- Compliance and integrity: Ensures data integrity and compliance with 21 CFR Part 11/EudraLex Annex 11 standards.
- Error reduction: Minimizes protocol-based errors through digitized test execution.
- Real-time insights: Provides instant visibility into all aspects of the process.
- Customization: Easily adapts to specific company needs without additional software.
The digital cleaning validation handbook
To learn more about adopting an automated and data-driven approach to cleaning validation at your organization, download our Digital Cleaning Validation Handbook today, authored by Kneat’s Senior Process Engineer, Amy Wilhite. Amy is a seasoned expert in cleaning and equipment validation, with years of firsthand experience managing various validation activities in life science manufacturing and biopharmaceutical production.







